There are several systems that have been put in place over time to enable individuals to identify themselves digitally. The eIDAS (for electronic identification and trust services) is the European regulation adopted to standardise and secure the use of digital identification.
So why is Wolfgang relying on eIDAS compliant service? And what is the eIDAS regulation?
Why is Wolfgang relying on eIDAS services?
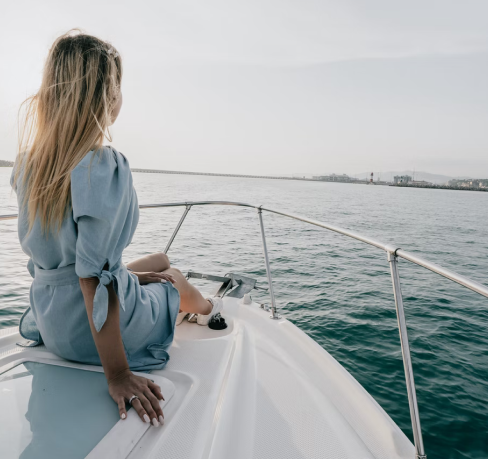
Wolfgang wants to provide a secure way for its users to sign and trust their contracts online. In order to prevent fraud, identity theft and other major inconveniences that plague the yacht chartering business, we went for the highest standard available for our level of compliance, which is eIDAS.
A signature on a paper contract, scanned then sent by email is not enough: if one cannot provide the paper version with the original signature (which is the case 99% of the time), it cannot be used in court to support the validity of the contract. Likewise, a Simple Electronic Signature (see after) provided without authentication of the signatory won’t be valid. Other “eContracts” on the market provide a false sense of security to their users without letting them know that in case of dispute, a court might not even recognise the validity of the document.
Wolfgang’s electronic authentication and signature provider is eIDAS-approved and ensures that our contracts are signed with an Advanced Electronic Signature so that you and your business are safe.
What is the eIDAS Regulation?
The eIDAS (Electronic IDentification And Trust Services) regulation is the regulation governing electronic identification and trust services for electronic transactions in the EU. It regulates electronic signatures, electronic transactions and involved bodies to provide a safer way for users to conduct business online
Specifically, the regulation defines the different levels of signatures and their requirements:
- Simple Electronic Signature: aka “click and sign” hardly more secure than a tick-box, this signature won’t make a contract worth more than a few hundred dollars enforceable.
- Advanced Electronic Signature: this signature requires the authentication of the signatory, the signatory then has sole control over his signature and if the document is tampered with, it will be invalidated.
- Qualified Electronic Signatures: same as Advanced plus the signatory must meet in person with an approved body to receive a token used for each signature. This is only used for the most secure applications.
This system improves security and convenience for both the signatory and the recipient: instead of depending on traditional and inconvenient methods or unsecure alternatives, such as appearing in person to sign paper-based contracts or emails and faxes, they can sign secured contracts across borders in one click.
The eIDAS Regulation guarantees a good level of security, and EU member states are required to recognise contracts signed by advanced electronic signatures that meet the standards with the same legal standing as contracts that are performed on paper.